Lecture notes - Belépés
4. Control points
In practice, control points represent the reference system. Control points
- are permanently and physically marked,
- their (1D, 2D or 3D) coordinates are known,
- are part of global, national or local networks.
Horizontal control points
Determination techniques can be:
- triangulation,
- traversing,
- GNSS-technique
The points are part of Geodetic Control Networks which are developed on a hierarchical basis. In Hungary, we distinguish the 1st (see the figure below), the 2nd, the 3rd and the 4th order networks. The average distance between the points is 30, 15, 7 and 4 km, respectively. In Hungary we have about 100 first ordered points and once we had about 100 000 horizontal control points in total. As a comparison, the area of Hungary is about 93 000 km2.
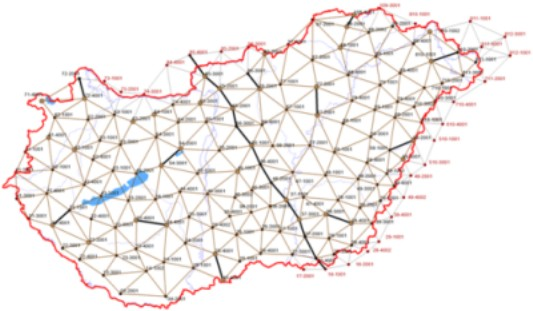
Points can be on the ground while other points are high in order to be able to sight them from a far distance.
Examples of establishing horizontal control points.



Examples of benchmarks.


Control points used on the spot of constructions

Online shop to browse and buy control points in Hungary (English interface is also available).
Network of active GNSS (or GPS) stations plays an important role in surveying these days. A great majority of land surveying jobs can be done based upon corrections from GNSS infrastructures.
More details about the Hungarian active GNSS network can found here: https://gnssnet.hu/. An alternative service provider is here: https://corrigo.hu/.