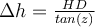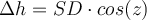Lecture notes
Lecture notes - Log in
6. Methods of vertical measurements
Definitions
- mean sea level
- reduced level
- relative heights in a building
Measurement methods
- levelling (optical, hydrostatic)
- trigonometrical height measurement
- physical methods
Levelling
In case of levelling a tangential line (or plane) of the equipotential surface is created by a suitable instrument. The instrument is called the surveyors’ level.
Principle of leveling
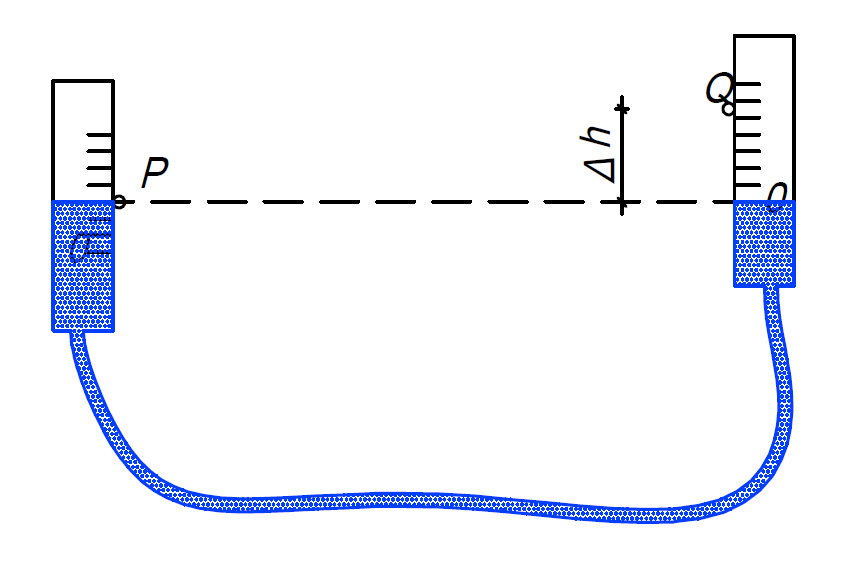
hydrostatic (based on the principle of communicating vessels)
optical:
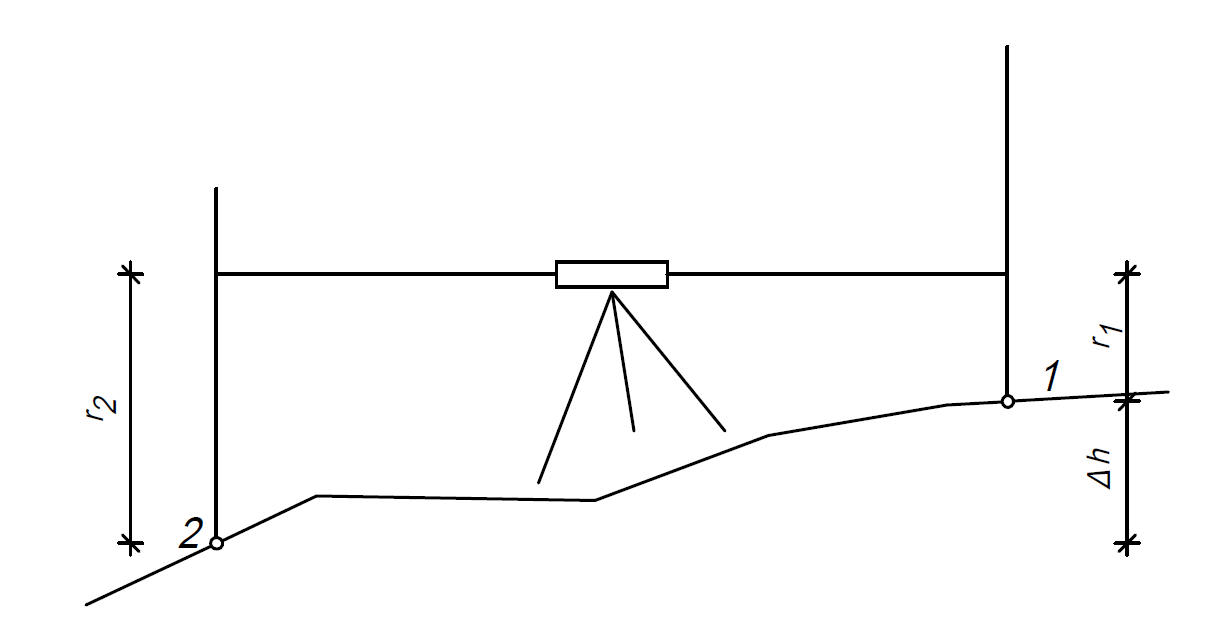
Reading on the leveling staff: Reading1, reading2, reading3, reading4
Getting the height difference: 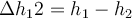
Type of levels
- tilting level
- automatic level
Major error sources - way of elimination
- collimation error - adjust your instrument on a regular basis
- tilting of the staff - use circulare bubble on the staff
- atmospheric effects - avoid strong sunshine, instable atmosphere
- settlement of the staff - use change plate
Aim of levelling: determine (1) new control points or (2) detail points.
Levelling methods
- line levelling
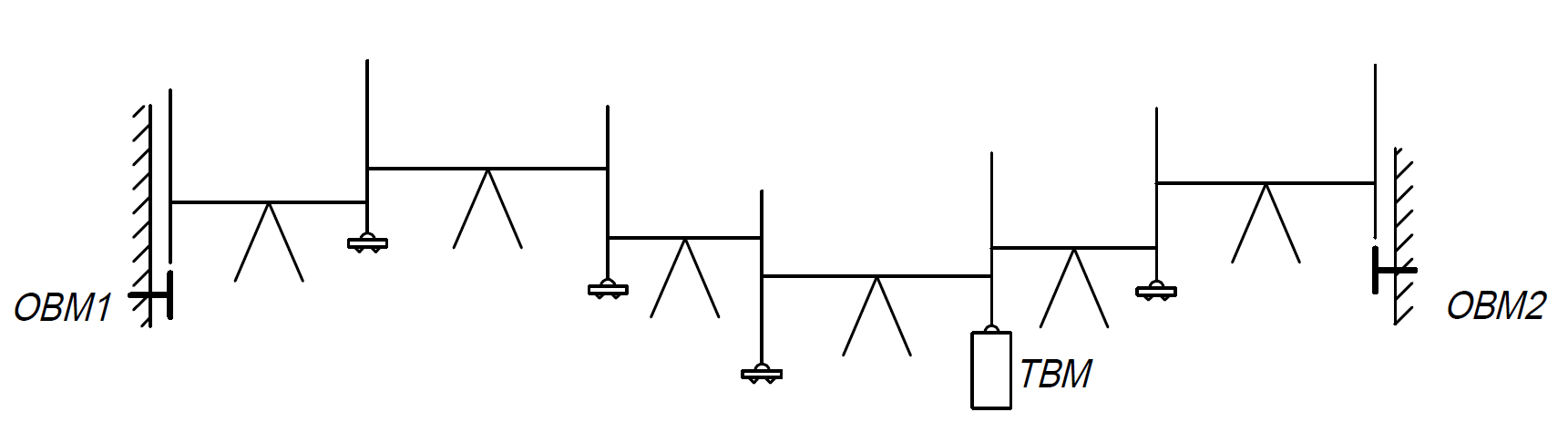
- long and cross sectional levelling
- grid levelling
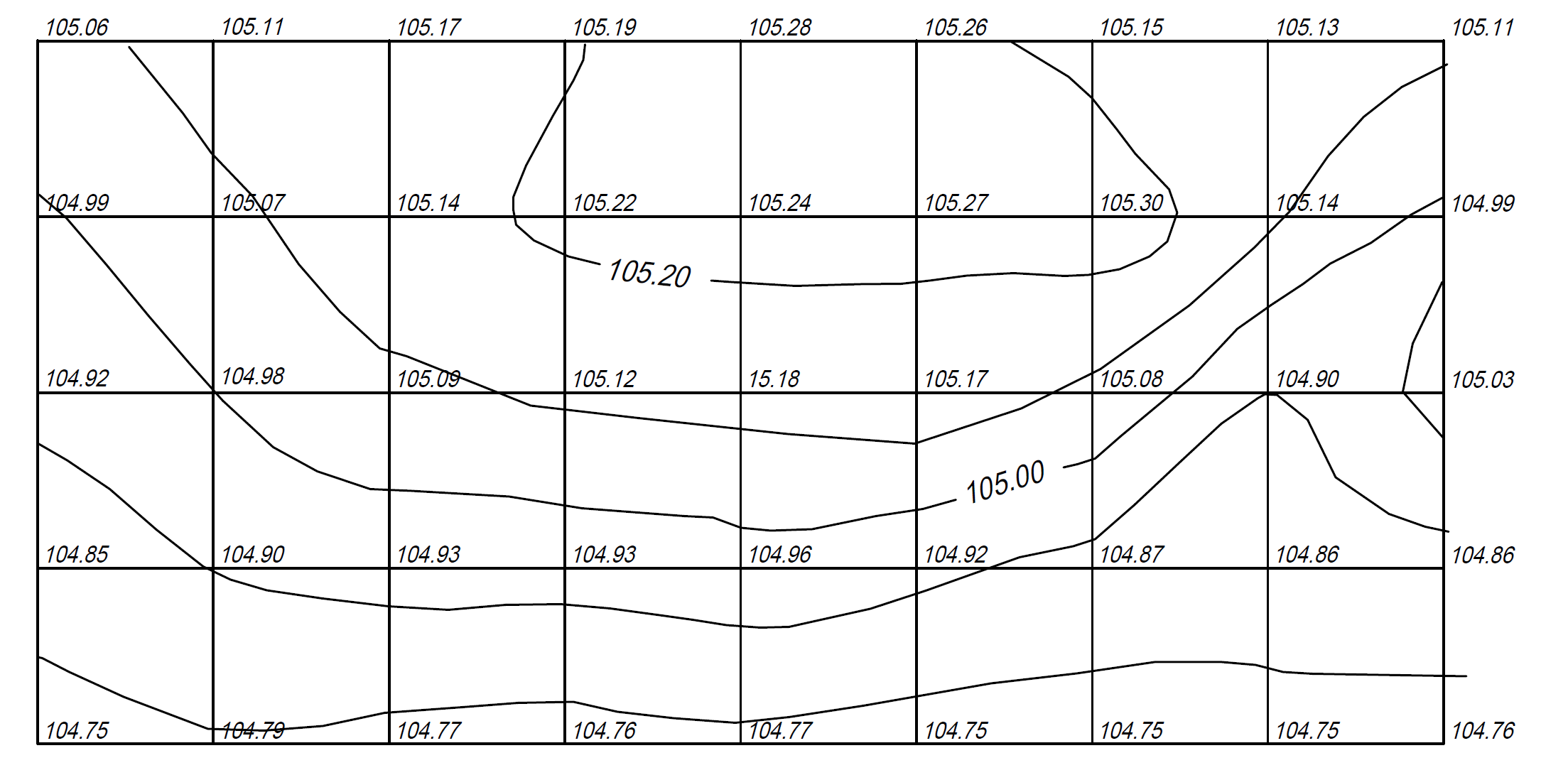
- detail point levelling
Trigonometric heighting
Principle, figure and formula
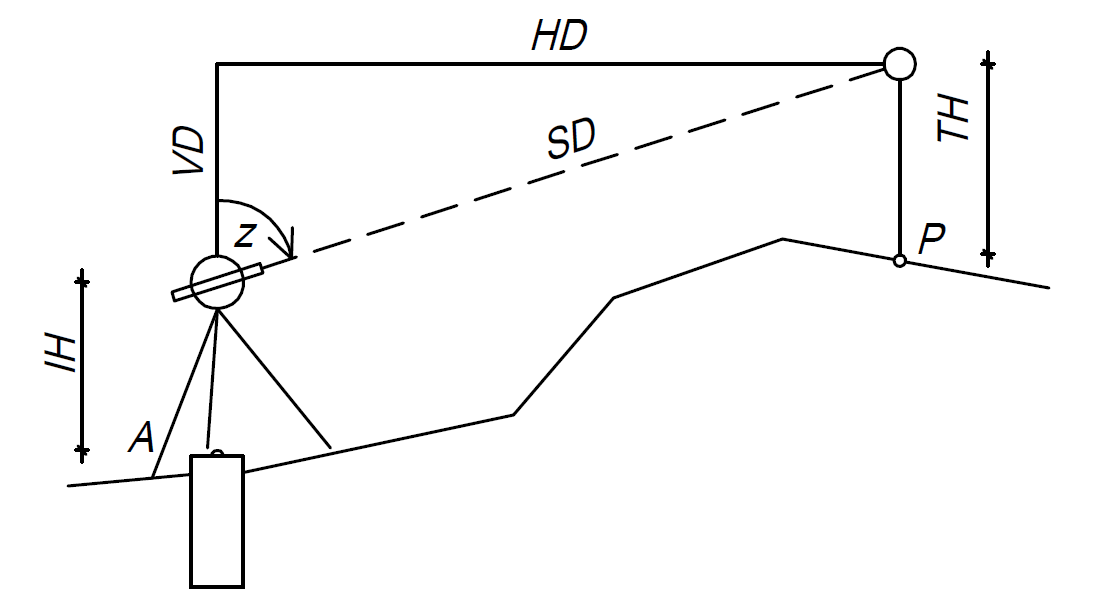
where
or
Advantages and disadvantages compared to levelling
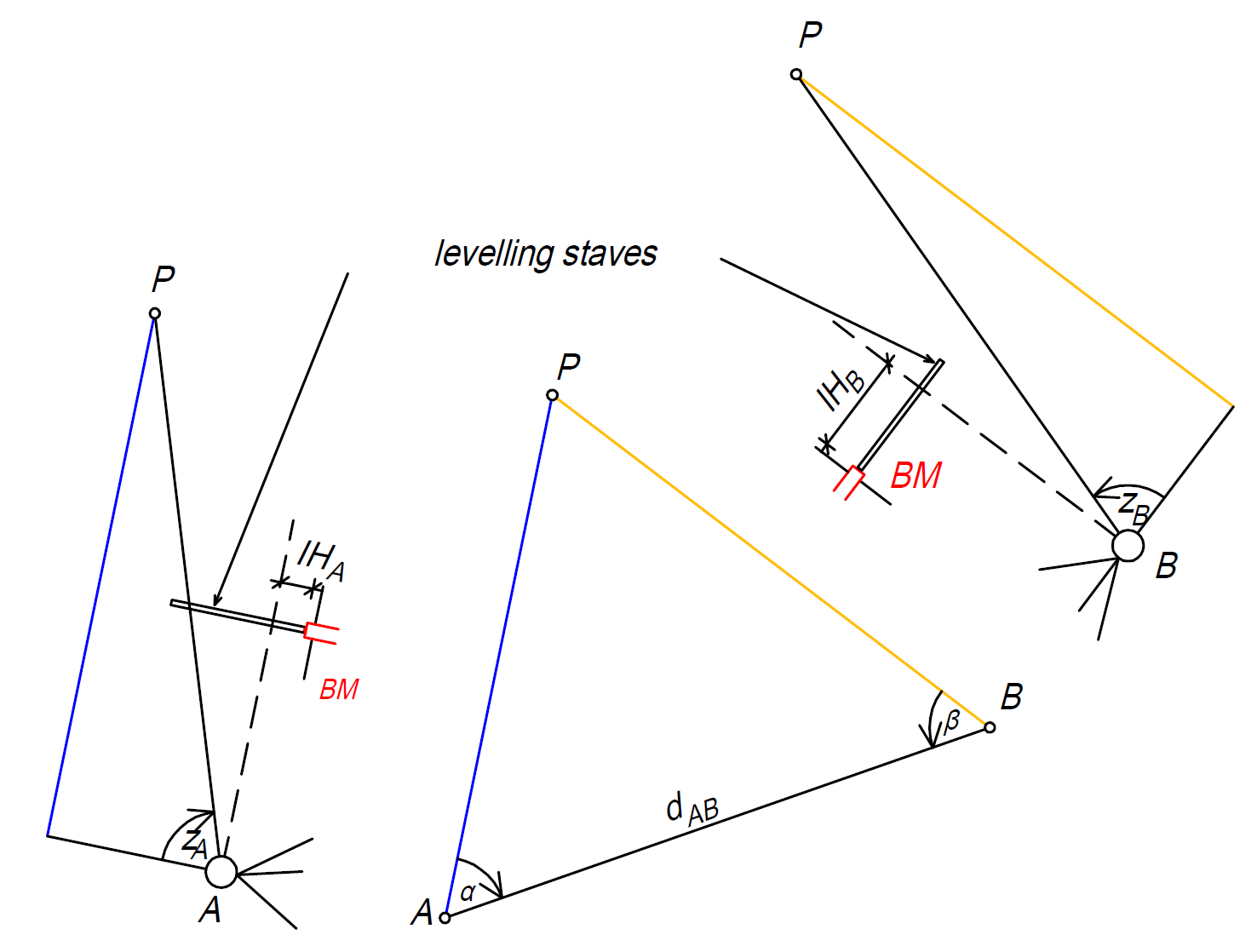
Measurement of the height of buildings using trigonometric heighting
Barometer for height measurement
Read the Bohr's story