Lecture notes
Lecture notes - Log in
8. GPS in land surveying
principle of GPS
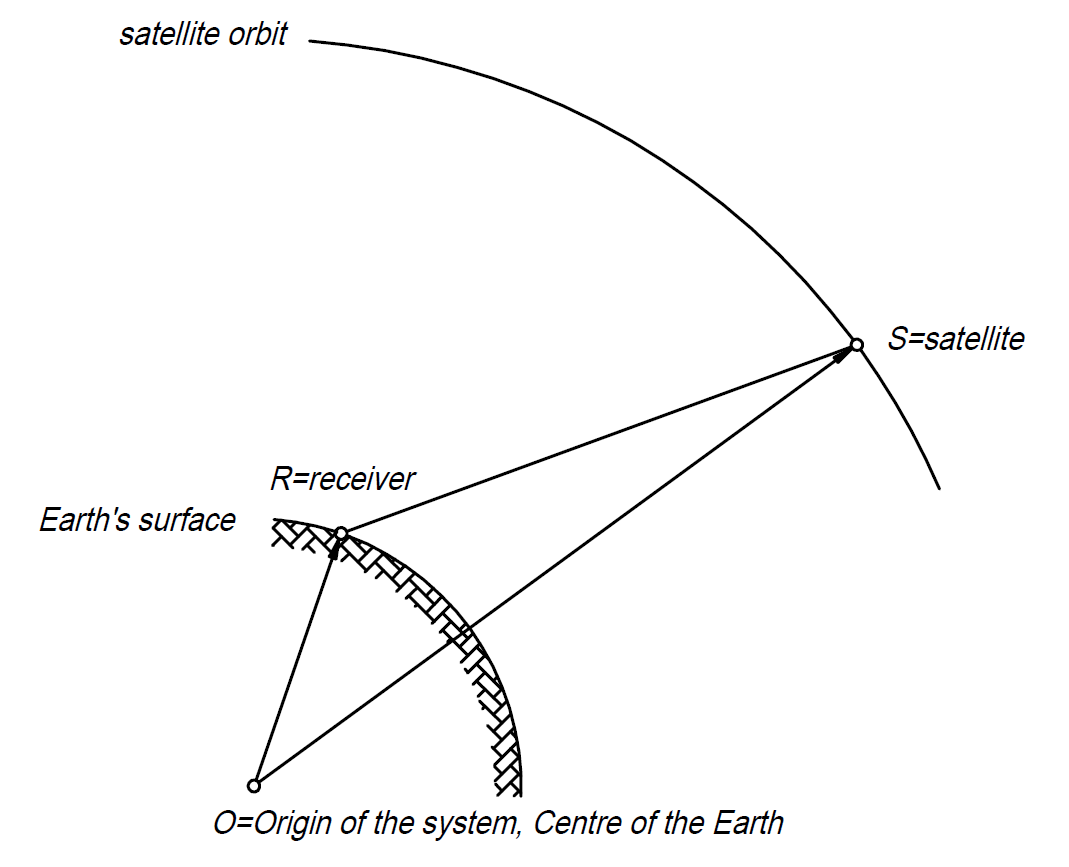
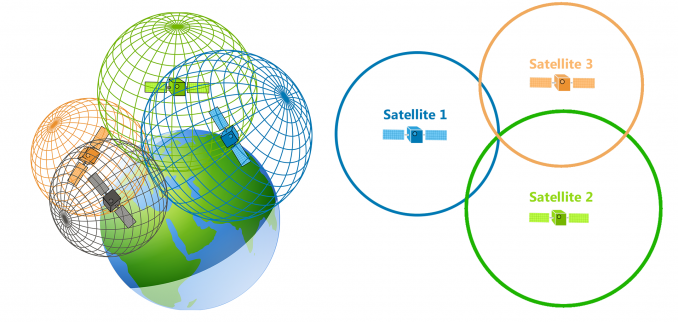
source: https://gisgeography.com/trilateration-triangulation-gps/
systems: GPS (31), Glonass (23), Galileo (22), Beidou (50), QZSS, IRNSS, EGNOS, WAAS ...
major error sources:
- orbit
- satellite clock offset
- atmosphere: troposphere and ionosphere
- receiver clock offset
- geometry, dilution of precision
- multipath
- jamming, spoofing
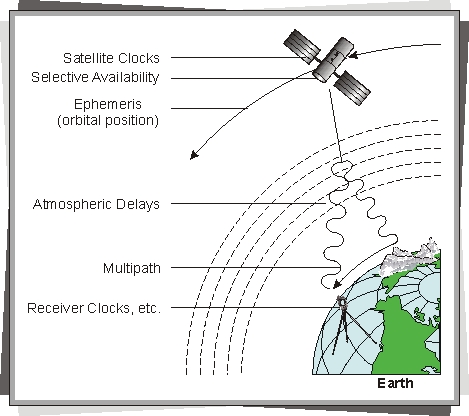
source: http://www.wirelessdictionary.com/Wireless-Dictionary-GPS-Errors-Definition.html
typical accuracy of everyday application versus accuracy requirement in land surveying
in order to reach cm accuracy:
- phase measurement instead of code one
- relative positioning instead of the absolute one
- real-time, communication between the base and rover receivers. Internet or radio.
- GNSS-infrastructure (e.g. https://www.gnssnet.hu/)
- transformation
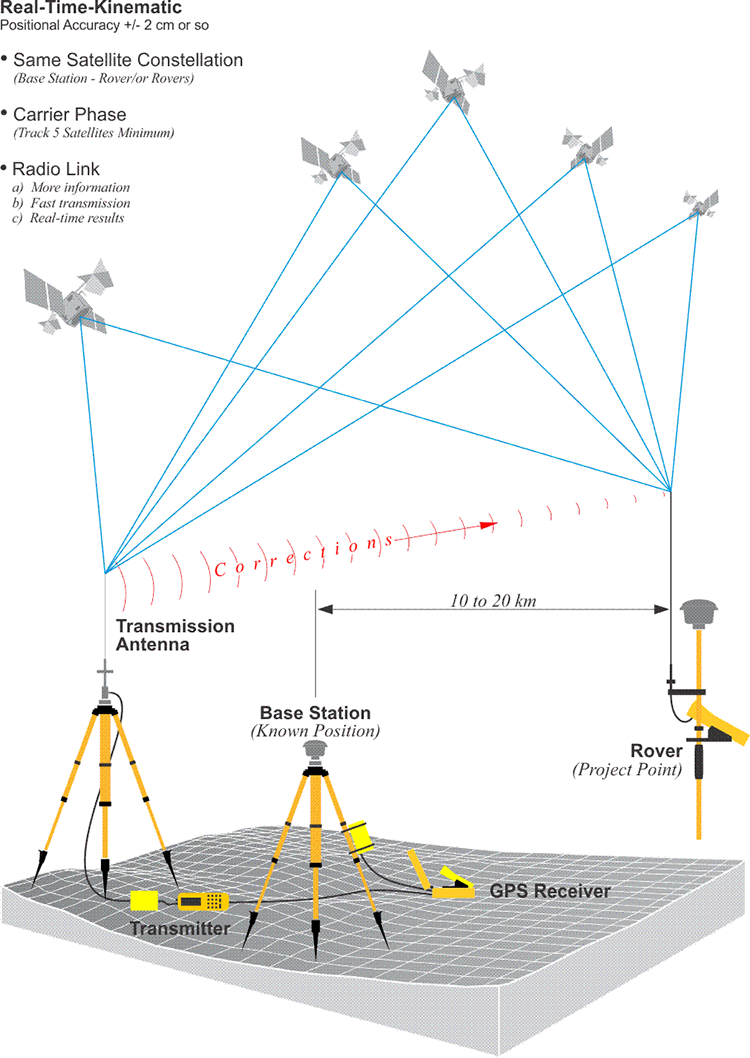
source: https://www.e-education.psu.edu/geog862/node/1725
Nowadays many projects in land surveying are done by GPS. It is not really expensive, it might be very efficient but not suitable for everything. Limitations:
- satellite visibility
- accuracy, especially the vertical one